Table Of Content
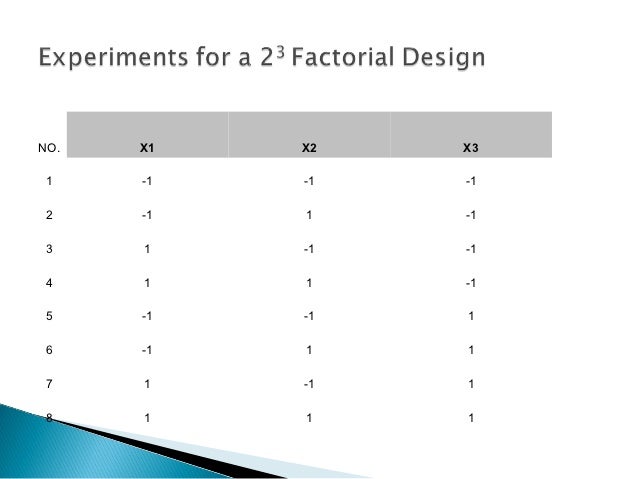
Such effects would be manifest in interactions amongst components (e.g., the effectiveness of a component might be reduced when it is paired with other components) or in increased data missingness. Moreover, if higher order interactions are not examined in models, researchers will not know if an intervention component is intrinsically weak (or strong) or is meaningfully affected by negative (or positive) interactions with other factors. It is tempting to take advantage of the efficiency of the factorial experiment and use it to evaluate many components since power is unrelated to the number of factors, and therefore, a single experiment can be used to screen many components. However, the number of factors used and the types and number of levels per factor can certainly affect staff burden. A 5-factor design with 2-levels/factor yields some 32 unique combinations of components (Table 1), and requires that at least five different active or “on” ICs be delivered. Moreover, if instead of “off” or no-treatment conditions, less intensive levels of components are used, then even more ICs must be delivered (albeit some of reduced intensity).
Factorial experiment
In the aquaculture experiment, the ordered triple (25, 80, 10) represents the treatment combination having the lowest level of each factor. In a general 2×3 experiment the ordered pair (2, 1) would indicate the cell in which factor A is at level 2 and factor B at level 1. If the number of combinations in a full factorial design is too high to be logistically feasible, a fractional factorial design may be done, in which some of the possible combinations (usually at least half) are omitted. From this table, we can see that there is positive correlation for factors A and C, meaning that more sleep and more studying leads to a better test grade in the class. Factor B, however, has a negative effect, which means that spending time with your significant other leads to a worse test score. The lesson here, therefore, is to spend more time sleeping and studying, and less time with your boyfriend or girlfriend.
Factorial design formulation optimization and in vitro characterization of curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for colon ... - ScienceDirect.com
Factorial design formulation optimization and in vitro characterization of curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for colon ....
Posted: Sat, 22 Feb 2020 23:13:55 GMT [source]
Main Effects
More formally, this means that the shoe and hat independent variables do not interact. It would mean that the effect of wearing a shoe on height would depend on wearing a hat. But in some other imaginary universe, it could mean, for example, that wearing a shoe adds 1 to your height when you do not wear a hat, but adds more than 1 inch (or less than 1 inch) when you do wear a hat.
Selecting the Right Factors and Components in a Factorial Design: Design and Clinical Considerations
For example, a researcher might choose to treat cell phone use as a within-subjects factor by testing the same participants both while using a cell phone and while not using a cell phone (while counterbalancing the order of these two conditions). But he or she might choose to treat time of day as a between-subjects factor by testing each participant either during the day or during the night (perhaps because this only requires them to come in for testing once). An example is a study by Halle Brown and colleagues in which participants were exposed to several words that they were later asked to recall (Brown, Kosslyn, Delamater, Fama, & Barsky, 1999)[1]. Some were negative health-related words (e.g., tumor, coronary), and others were not health related (e.g., election, geometry). In general, when dummy coding is used, the effects corresponding to main effects in a standard ANOVA are similar to simple effects, i.e., the effect of a variable when all other variables in the model are set to the level coded as zero.
Design of self-healing styrene-butadiene rubber compounds with ground tire rubber-based reinforcing additives by ... - ScienceDirect.com
Design of self-healing styrene-butadiene rubber compounds with ground tire rubber-based reinforcing additives by ....
Posted: Fri, 01 Jul 2022 05:57:49 GMT [source]
When there are two independent variables, each with two levels, there are four total conditions that can be tested. It has been argued that factorial designs epitomize the true beginning of modern behavioral research and have caused a significant paradigm shift in the way social scientists conceptualize their research questions and produce objective outcomes (Kerlinger & Lee, 2000). Factorial design can be categorized as an experimental methodology which goes beyond common single-variable experimentation. In the past, social scientists had been transfixed on singular independent variable experiments and foreshadowed the importance of extraneous variables which are able to attenuate or diminish research findings.
Replies to “A Complete Guide: The 2×2 Factorial Design”
You would measure combination effects of \(A\) and \(B\) (a1b1, a1b2, a2b1, a2b2). Since we have two factors, each of which has two levels, we say that we have a 2 x 2 or a 22 factorial design. Typically, when performing factorial design, there will be two levels, and n different factors. The factorial design, as well as simplifying the process and making research cheaper, allows many levels of analysis. As well as highlighting the relationships between variables, it also allows the effects of manipulating a single variable to be isolated and analyzed singly. Agricultural science, with a need for field-testing, often uses factorial designs to test the effect of variables on crops.

Types of Factorial Design
Again, because neither independent variable in this example was manipulated, it is a non-experimental study rather than an experimental design. This is important because, as always, one must be cautious about inferring causality from non-experimental studies because of the threats of potential confounding variables. For example, an effect of participants’ moods on their willingness to have unprotected sex might be caused by any other variable that happens to be correlated with their moods. Factorial design is a type of research methodology that allows for the investigation of the main and interaction effects between two or more independent variables and on one or more outcome variable(s). In addition to looking at the employment sector, the researchers also look at gender.
When 40 year olds, however, are given a 5 mg pill or a 10 mg pill, 15% suffer from seizures at both of these dosages. There is an increasing chance of suffering from a seizure at higher doses for 20 year olds, but no difference in suffering from seizures for 40 year olds. Thus, there must be an interaction effect between the dosage of CureAll, and the age of the patient taking the drug. When you have an interaction effect it is impossible to describe your results accurately without mentioning both factors.
These plots are different ways to present the statistical results of the analysis. Examples of these plots can be found in the Minitab Example for Centrifugal Contactor Analysis. The alpha value, which determines the limit of statistical significance, can be chosen in this menu also.
In addition, the use of a large number of factors allows for built-in evaluations of the robustness of the main effects of the ICs. This is because, as noted earlier, such effects are determined by averaging over the other component effects (with effect coding). To illustrate a 3 x 3 design has two independent variables, each with three levels, while a 2 x 2 x 2 design has three independent variables, each with two levels. A 2×2 factorial design is a type of experimental design that allows researchers to understand the effects of two independent variables (each with two levels) on a single dependent variable. In Chapter 1 we briefly described a study conducted by Simone Schnall and her colleagues, in which they found that washing one’s hands leads people to view moral transgressions as less wrong [SBH08]. In a different but related study, Schnall and her colleagues investigated whether feeling physically disgusted causes people to make harsher moral judgments [SHCJ08].
Similarly, if we made a separate graph for the main effect of hats then we should see a difference of 6 between conditions. The potential for statistical interaction, ie, when the effect of an intervention depends on the presence or absence of another intervention, is both a strength and a limitation. The strength is that the question of differential effects may actually be of scientific and clinical interest. The experimental study design can be classified into 2 groups, that is, controlled (with comparison) and uncontrolled (without comparison).1 In the group without controls, the outcome is directly attributed to the treatment received in one group.
No comments:
Post a Comment